Creatinine is a waste product formed when muscles use energy. Healthy kidneys filter it from the blood and excrete it through urine. When a blood test shows high creatinine, it does not automatically mean kidney failure.
Creatinine is a signal, not a diagnosis. Its interpretation depends on:
- Age
- Sex
- Muscle mass
- Hydration status
- Medications and supplements
- Trend over time
This explains why two people with the same creatinine value can have very different kidney health outcomes.
What is creatinine?
Creatinine is a waste product of muscle normal functioning. It is a break down product of creatine phosphate and is incorporated in the muscles as energy source. The larger the mass of the muscles, the larger the creatinine levels. It is because of this reason that males have a higher level of creatinine compared to females. The most common means of the body in eliminating creatinine in the blood is through filtration in the kidneys and subsequent elimination in the urine.
Normal vs High Creatinine Levels 2026
Normal Creatinine Ranges
| Group | Normal Range (mg/dL) |
| Adult Men | 0.7 – 1.3 |
| Adult Women | 0.6 – 1.1 |
| Elderly (65+) | Up to 1.4 |
| Athletes / High muscle mass | May appear higher |
How High Creatinine Affects Kidney Function
Creatinine rises when kidneys filter blood more slowly. Doctors interpret this using eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate).
Creatinine vs eGFR Interpretation
| Creatinine Level (mg/dL) | eGFR Range | Clinical Meaning |
| ≤ 1.2 | ≥ 90 | Normal kidney function |
| 1.3 – 1.6 | 60 – 89 | Mild reduction |
| 1.7 – 2.0 | 30 – 59 | Moderate impairment |
| > 2.0 | < 30 | Severe kidney dysfunction |
Creatinine vs eGFR Trend
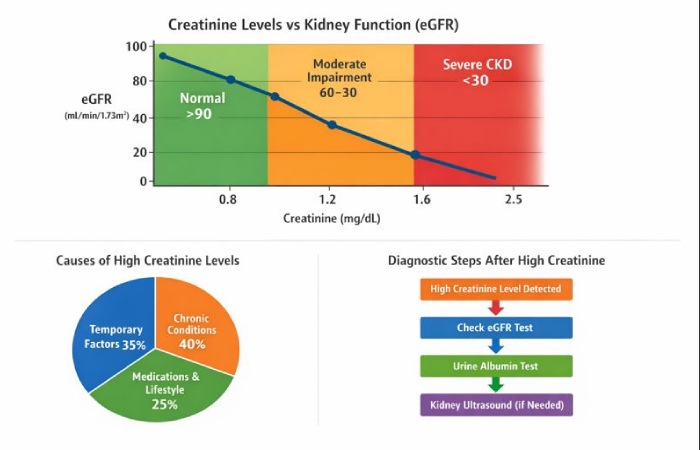
Causes of High Creatinine
Causes of High Creatinine</strong>
| Category | Examples | Reversible? |
| Temporary | Dehydration, intense exercise | Yes |
| Lifestyle | High‑protein diet, creatine supplements | Often |
| Medication‑related | NSAIDs, certain antibiotics | Sometimes |
| Medical | CKD, diabetes, hypertension | Often chronic |
| Acute injury | Infection, obstruction, trauma | Depends |
Distribution of Causes of High Creatinine
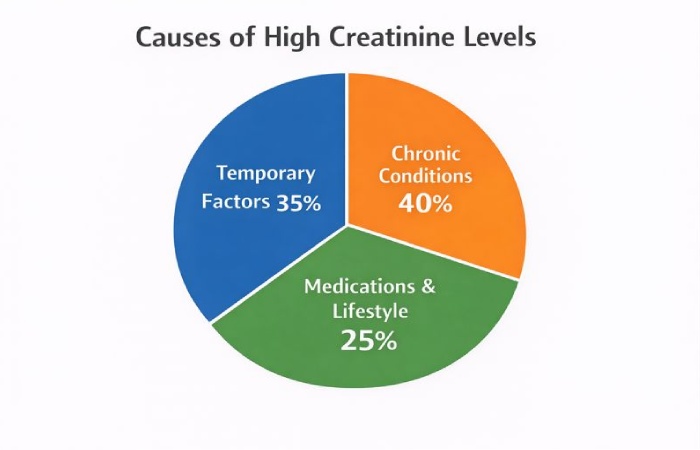
Key insight: Not all high creatinine levels indicate permanent kidney damage.
Symptoms: Why Many People Feel Normal
High creatinine often causes no symptoms in early stages.
Progression of Symptoms
- Early: No symptoms
- Mid‑stage: Fatigue, swelling of feet, foamy urine
- Advanced: Breathlessness, confusion, severe itching, nausea
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Fitness
- Creatinine: 1.6 mg/dL
- Cause: High‑protein diet + creatine supplements
- eGFR: Normal
- Outcome: Levels normalized after stopping supplements
Study 2: Middle‑Aged Diabetic Patient
- Creatinine: 1.4 mg/dL
- eGFR: 58
- Diagnosis: Early chronic kidney disease
- Outcome: Stabilized with blood sugar and BP control
Study 3: Chronic Painkiller Use
- Gradual creatinine rise over 2 years
- Cause: Long‑term NSAID use
- Outcome: Partial improvement after stopping medication
Doctors Recommend Tests After High Creatinine
Diagnostic Follow‑Up Tests
| Test | Purpose |
| Repeat fasting creatinine</td> | Rule out dehydration |
| eGFR | Assess filtration rate |
| Urine albumin‑creatinine ratio | Detect early kidney damage |
| Kidney ultrasound | Identify structural issues |
Can High Creatinine Be Reduced?
Evidence‑Based Actions
- Proper hydration
- Blood pressure control
- Blood sugar management
- Avoid unnecessary painkillers
- Treat underlying kidney conditions
Myths vs Facts
| Myth | Fact |
| Detox drinks lower creatinine</td> | No clinical evidence |
| High creatinine always means dialysis | False in most cases |
| Herbal remedies cure kidney disease | Unsupported and risky |
| Drinking water reverses CKD | Helps hydration, not damage |
When to Worry and When Not To
Usually not urgent if:
- Mild elevation
- Normal eGFR
- No symptoms
Seek medical care if:
- Rapid rise in creatinine</li>
- eGFR < 30
- Swelling, breathlessness, confusion
Treatments
Treatment of high creatinine level is dependent on the cause. In cases where high levels of creatinine are caused by kidney infection, they ought to be brought down to normal levels by taking an antibiotic. Similarly, in case the raised creatinine level is a resultant of high blood pressure then medication to cure the same should reduce creatinine levels as well. The doctors can also prescribe alteration of daily habits, which is based on the reason like lessening of protein intake and increasing the dietary fibre. This can make one control their creatinine levels.
Final Takeaway
High creatinine is a warning light, not a verdict. When interpreted with eGFR, trends, and clinical context, it enables early kidney protection and prevents long‑term damage.