Salmonella
Salmonella infection (salmonellosis) is a joint bacterial disease that affects the gut. However, these bacteria are commonly found in the intestines of animals and humans and are excreted in the faeces. Moreover, people are most often infected with contaminated water or food.
All in all, people with Salmonella infection usually have no indications. Whereas, others grow diarrhoea, fever, and abdominal cramps within 8 to 72 hours. And also, most vigorous people recover within a few days without special treatment.
In some cases, diarrhoea associated with a Salmonella infection can dehydrate that immediate medical attention is required. And also, if the infection spreads outside the gut, life-threatening complications can also develop. Furthermore, the risk of contracting Salmonella is greater if you travel to countries with poor hygiene.
Salmonella Enterocolitis
Salmonella enterocolitis is bacterial infection of the lining of the small intestine caused by Salmonella bacteria. However, it is a type of food poisoning.
Causes of Salmonella Enterocolitis
Salmonella infection is one of the most common types of food poisoning. Furthermore, it happens when you eat food or drink water that contains this bacteria.
However, Salmonella germs can enter food in a variety of ways.
You are more likely to get this type of infection if:
1.Eat foods such as turkey, turkey dressing, chicken, or eggs that have not been cooked well
or stored properly
2. Are around family members with a recent salmonella infection
3. Have been in or worked in a hospital, nursing home, or another long-term health facility
4. Have a pet iguana or other lizards, turtles, or snakes
(reptiles and amphibians can be carriers of Salmonella)
5. Handle live poultry
6. Have a weakened immune system
7. Regularly used medicines that block acid production in the stomach
8. Have Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis
9. Used antibiotics in the recent past
Reasons for Salmonella Enterocolitis
Salmonella bacteria live in the intestines of humans, animals, and birds. Mostly, people become infected with it by eating stool-contaminated food.
Moreover, commonly infected foods include:
1. Raw Meat, Poultry, and Seafood
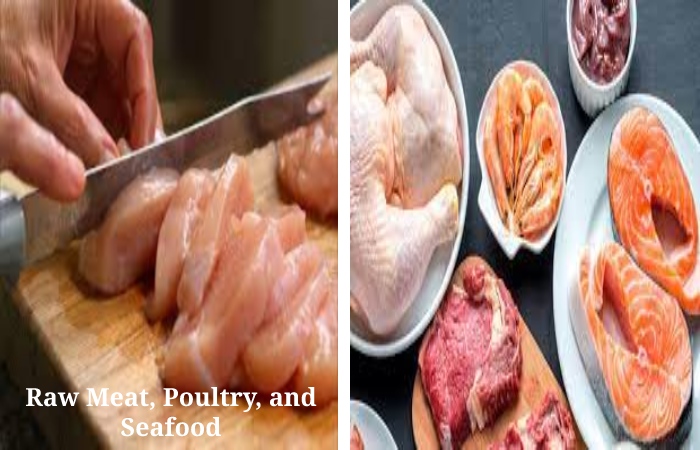

Faeces can settle on raw meat and poultry during slaughter. Moreover, Seafood can be contaminated if collected from contaminated water.
2. Raw Eggs
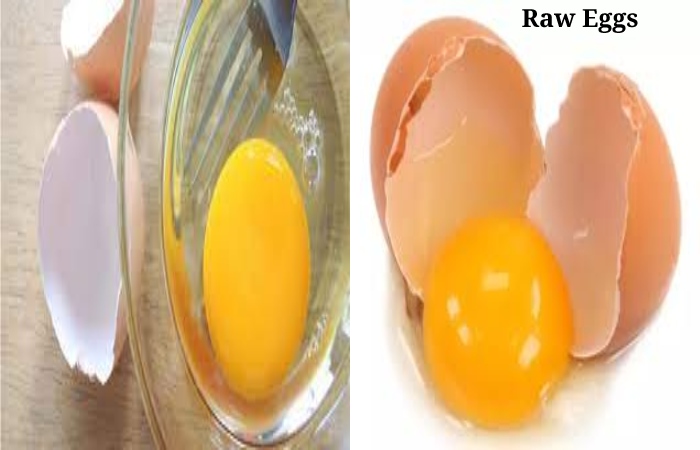

While eggshells may seem like an ideal barrier to infection, some infected chicks produce eggs containing Salmonella even before the shell is formed.
Moreover, Raw eggs are used in homemade varieties of mayonnaise and hollandaise sauce.
3. Fruits and Vegetables.
Some fresh produce mainly imported produce, can be moistened or washed during treatment with salmonella-contaminated water.
Moreover, adulteration can also happen in the kitchen when raw meat and poultry juices come into contact with raw foods such as salads.
Additionally, the FDA also points out that some outbreaks of Salmonella have been linked to contaminants in spices. So, the agency is looking for ways to improve the safety of spices.
And also, many foods become filthy when prepared by people who do not wash their hands after using the toilet or changing diaper.
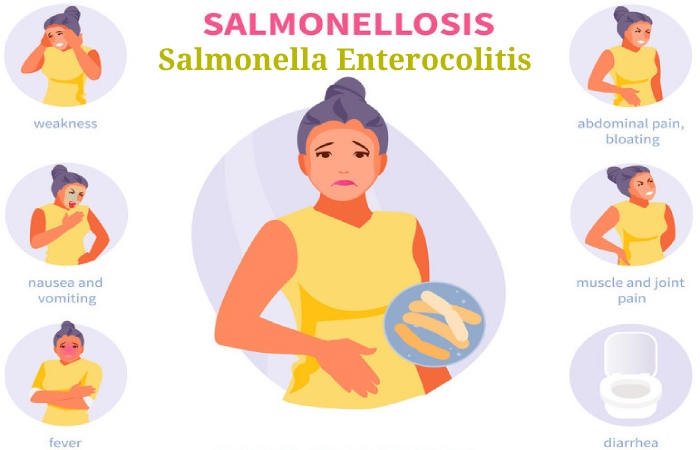
Symptoms of Salmonella Enterocolitis
Salmonella infection is usually produce by eating raw or undercooked meat, poultry, eggs, or egg products. And also, the incubation period differs from a few hours to two days.
However, most of its contaminations can be classified as stomach flu (gastroenteritis).
Possible Signs and Symptoms include:
- Nausea (vomiting)
- Vomiting (Nausea)
- Abdominal contractions
- Looseness of the bowels
- Fever (Temperature)
- Chills (Anxieties)
- Headache
- Blood in the stool (feces)
The signs and indications of its infection usually last two to seven days. Furthermore, Diarrhoea can last up to 10 days, although it can take several months for your bowels to return to normal.
And also, some species of Salmonella bacteria cause typhoid fever, an sometimes fatal disease that is more common in developing countries.
However, the infection can also arise if you touch something infected, including pets, especially birds and reptiles, and then stick your fingers in your mouth.
Risk Factors of Salmonella
Factors that can increase the risk of contracting Salmonella include activities that can lead to closer contact with this bacteria. And also, health problems can weaken overall resistance to infection.
1. Increase Exposure
Travelling Abroad
Salmonella infection, including the species that causes typhoid fever, is more common in developing countries with poor sanitation.
Possession of Poultry or Reptiles
Some pets, especially birds and reptiles, can carry salmonella bacteria.
2. Diseases of the Stomach or Intestines
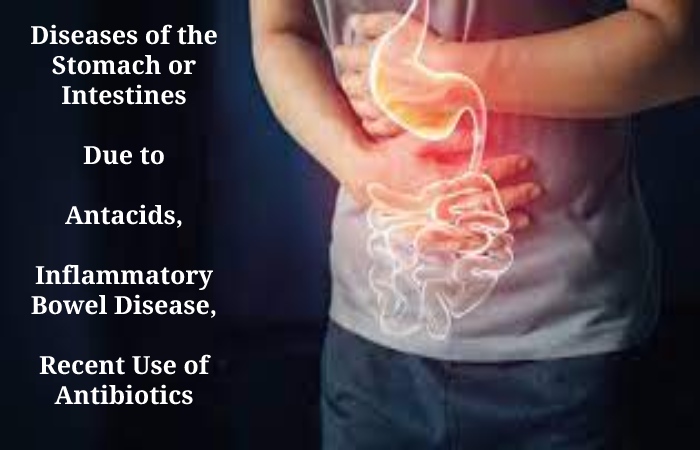
Your body has many natural defence mechanisms in contradiction of salmonella contamination. For example, strong stomach acid can destroy many kinds of salmonella bacteria. But, some medical or drug problems can short-circuit this natural defence. Examples included:
Antacids
Reduced stomach acid allows more salmonella bacteria to survive.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
This disease damages the intestinal lining, which makes it easier for salmonella bacteria to spread.
Recent Use of Antibiotics
It can reduce the number of “good” bacteria in your intestines, which may impair your ability to fight off its infection.
3. Immune Problems
The following health or medication problems appear to increase the risk of contracting Salmonella due to a compromised immune system.
- AIDS
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Malaria
- Refusal of drugs taken after organ transplantation
- Corticosteroids
Complications of Salmonella Enterocolitis
Salmonella infection is usually not life-threatening. However, complications can be dangerous for some people, especially infants and young children, the elderly, transplant recipients, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems.
1. Dehydration
If you can’t drink enough to replace the fluid loss due to persistent diarrhoea, you may become dehydrated. Warning signs include:
- Decreased urine production
- Dry mouth and tongue
- Sunken eyes
- Reduced tear production
2. Bacteremia
If Salmonella infection enters the bloodstream (bacteremia), it can infect tissues throughout the body, including:
- Tissue adjacent to the brain and spinal cord (meningitis)
- The lining of the heart or valves (endocarditis)
- Your bones or bone marrow (osteomyelitis)
- The lining of blood vessels, especially if you have had a vascular graft.
3. Reactive Arthritis
People who have had it have a higher risk of developing reactive arthritis. Reactive arthritis, also known as Reiter’s syndrome, usually causes:
- Eye irritation
- Painful urination
- Painful joints
Prevention from Salmonella Enterocolitis
Basically, the Ministry of Agriculture has developed an Action Plan for Salmonella, which includes upgrading the poultry slaughter inspection system and improving sampling and testing programs for poultry and meat. However, the plan aims to decrease the incidence of Salmonella infections in the United States.
You can also be careful not to pass the bacteria on to other people. Moreover, Preventive methods are especially important when preparing food or caring for infants, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems. So, make sure you cook food thoroughly and refrigerate or freeze it quickly.
1.Wash Your Hands
Thorough hand washing can help prevent the bacteria from getting into your mouth or any food you prepare. Wash your hands after:
- Firstly, when you use the bathroom
- Secondly, while changing a diaper
- Work with raw meat or poultry
- Clean up pet faeces
- Lastly, when you touch reptiles or birds
2. Keep Things Separate
To prevent cross-contamination:
- Store raw meat, poultry, and seafood separately from other foods in the refrigerator.
- If possible, keep two cutting boards in your kitchen, one for raw meat and one for fruits and vegetables.
- Never put cooked food on an unwashed plate that used to have raw meat on it.
3. Avoid Eating Raw Eggs
Cookie doughs, homemade ice cream, and sauces contain raw eggs. And also, if you need to eat raw eggs, make sure they have been pasteurized.
Also Read: Ajwain – Names in other languages, 9 Benefits For Hair, Skin, and Health
Related Searches:
[symptoms of salmonella]
[treatment of salmonella]
[what causes salmonella]
[salmonella poisoning]
[salmonella prevention]
[how to prevent salmonella]
[salmonella sources]
[salmonella food poisoning]